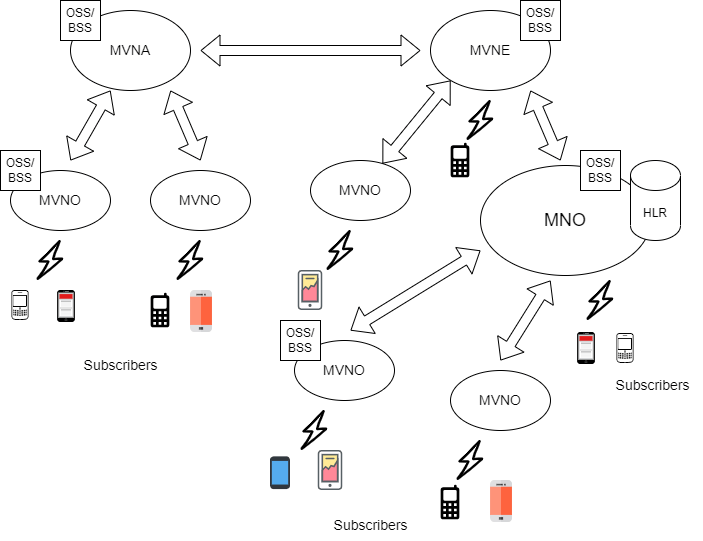
Jargon and acronyms are common in the constantly changing realm of telecommunications, making it difficult for insiders and customers to stay current. The phrases MVNO | MVNE | MNO | MVNA are some of the most typical ones you’ll run against. These abbreviations stand for important telecom ecosystem participants, each of whom contributes uniquely to the development of the wireless industry. The differences between MVNOs, MVNEs, MNOs, and MVNAs, as well as how they work together to provide wireless services, will be clarified in this blog article as we sort through the telecom alphabet soup.
MNO – Mobile Network Operator
Starting with the most fundamental phrase, Mobile Network Operator (MNO), let’s dissect it. The leading companies in the telecom sector are MNOs. They are responsible for maintaining and owning the physical network that enables wireless communication. The backbone of the wireless network comprises this infrastructure, which also comprises cell towers, base stations, switches, and backhaul networks.
These networks must be built and maintained by MNOs to provide countrywide or regional coverage. Popular MNOs include Verizon Wireless, AT&T, T-Mobile, and Vodafone.
MNOs allot frequency spectrum, create technical guidelines, and make significant R&D investments to enhance their networks. In addition, they oversee regulatory compliance, customer service, and billing. MNOs serve as the structural support for the whole wireless communication ecosystem.
MVNO – Mobile Virtual Network Operator
Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs) do not possess their physical network infrastructure, unlike MNOs. Instead, they rent access to the network from MNOs. In essence, MVNOs are wireless service resellers. They purchase network capacity wholesale prices from one or more MNOs and then market these services to their clients under their brand.
MVNOs come in various shapes and sizes, serving diverse market sectors and niches. While some MVNOs specialize in data-only services, others provide prepaid plans. Boost Mobile, Cricket Wireless, and TracFone are a few MVNOs. Because they don’t have to invest as much in infrastructure as MNOs do, these businesses often provide more pricing and plan options flexibility.
MVNE – Mobile Virtual Network Enabler
MVNEs are less well-known but significant players in the background. They help MVNOs run efficiently by offering them the required services and support. As a middleman between MVNOs and MNOs, MVNEs make it easier for MVNOs to access the network and its components.
MVNEs offer a range of services, including:
Billing and Customer Support:
On behalf of MVNOs, MVNEs frequently undertake invoicing and customer support tasks. This might involve handling client queries, processing payments, and monitoring prepaid balances.
Provisioning:
Besides handling the technical facets of connecting clients to the network, MVNEs help MVNOs supply SIM cards, activate devices, and manage customer connectivity.
Reporting and Analytics:
About network utilization, consumer behaviour, and performance metrics, MVNEs offer MVNOs insightful data.
Wholesale Rate Negotiations:
For MVNOs to provide competitive pricing to their clients, MVNEs assist MVNOs in obtaining favourable wholesale rates from MNOs.
MVNA – Mobile Virtual Network Aggregator
Another layer of the telecom ecosystem comprises Mobile Virtual Network Aggregators (MVNAs), which act as middlemen to combine several MVNOs into a single platform. This aggregation streamlines numerous operational issues and makes it easier to link MVNOs to MNOs.
MVNAs offer several advantages to MVNOs, including:
Simplified Access:
The difficulty of negotiating agreements and integrating with several networks is reduced by MVNAs, which offer a single entry point to numerous MNOs.
Economies of Scale:
MVNAs can use their combined purchasing power to pressure MNOs to lower their wholesale prices, saving them money.
Technical Integration:
Since MVNAs frequently provide standardized APIs and technological integration solutions, connecting to various networks is made simpler for MVNOs.
Enhanced Service Portfolio:
MVNAs may provide MVNOs with broader features and services, including international roaming and value-added services.
Conclusion
Anyone trying to negotiate the complicated world of telecommunications has to be aware of the differences between MVNOs, MVNEs, MNOs, and MVNAs. MNOs supply the infrastructure, MVNOs provide cellular services, MVNEs support MVNO operations, and MVNAs make it easier for MVNOs to connect to the internet and run their business.
These numerous organizations collaborate to develop a vibrant and competitive wireless industry that offers consumers a variety of service choices and costs. These jobs could alter and adapt as the telecom industry develops to fulfil the needs of a constantly connected society. However, cooperation among MVNO | MVNE | MNO | MVNA will continue to be crucial to providing dependable and cutting-edge wireless services to clients worldwide.





